optimization
Lectura de dos PFC's a la DE sobre oferta òptima als mercats d'energia elèctrica.
Wed, 07/22/2009 - 16:25 — admin
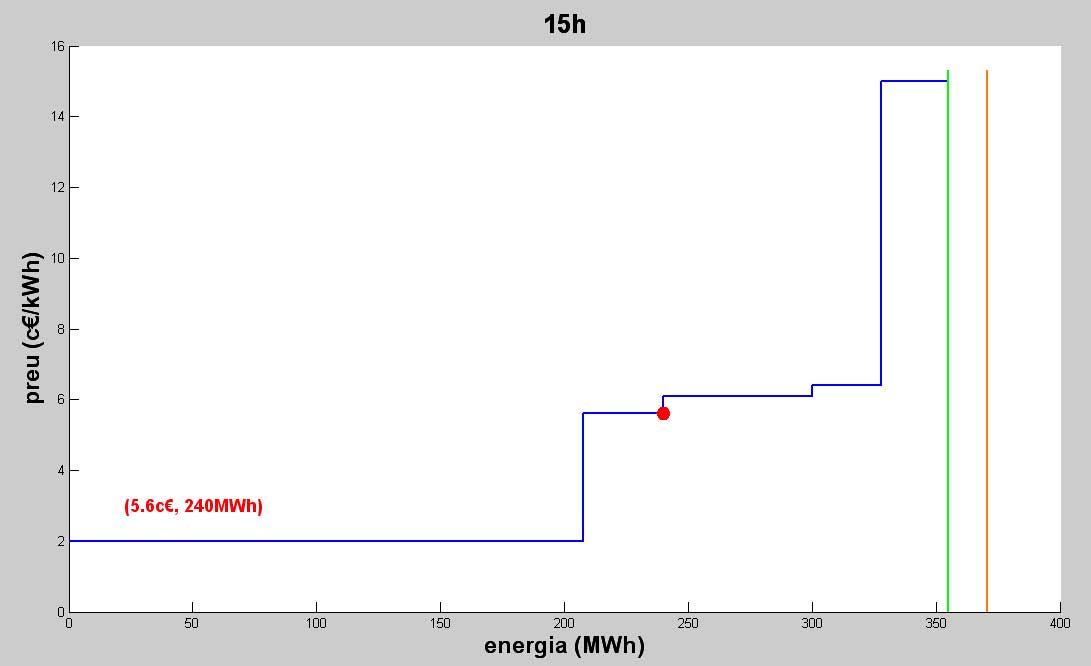
El passat dijous 9 de juliol de 2009 es va llegir el Projecte Final de Carrera dels alumnes Silvia Nieto i Ivan Ruz, que portava per títol "Estudi i optimització de l’oferta al Mercat Ibèric ’Electricitat (MIBEL)", dirigit pel professor Javier Heredia. Els objectius del treball han estat:
- Fer una descriptiva de les dades obtingudes de les energies tèrmiques per veure el comportament que hi tenen.
- Entendre el model d'optimització d'oferta presentat a l'article [1], i compendre la seva implementació.
- Entendre el model d'optimització d'oferta de l'article [2] i resoldre una nova modelització adaptant aquest model a l'anterior fent els canvis pertinents.
- Comparar els dos models i treure'n conclusions sobre quin és el més eficient.
[1] Arroyo, José M. ; Carrión, Miguel. A computationally efficient mixed-integer linear formulation for the termal unit commitment problem. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers transactions on power systems, vol. 21, nº3, agost 2006.
[2] "A Stochastic Programming Model for the Thermal Optimal Day-Ahead Bid Problem with Physical Futures Contracts", Submitted to European Journal of Operations Research, Barcelona, Espanya, Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, 03/2009
A Stochastic Programming Model for the Thermal Optimal Day-Ahead Bid Problem with Physical Futures Contracts
Wed, 03/18/2009 - 17:25 — admin| Publication Type | Report |
| Year of Publication | 2009 |
| Authors | Cristina Corchero; F. Javier Heredia |
| Pages | 19 |
| Date | 03/2009 |
| Reference | Research Report DR 2009/03, Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research, E-Prints UPC http://hdl.handle.net/2117/2795, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya |
| Prepared for | Accepted for publication at Computers and Operations Research |
| City | Barcelona, Spain. |
| Key Words | research; Stochastic programming; OR in energy; electricity day-ahead market; futures contracts; optimal bid |
| Abstract | The reorganization of the electricity industry in Spain completed a new step with the start-up of the Derivatives Market. One main characteristic of MIBEL’s Derivatives Market is the existence of physical futures contracts; they imply the obligation to settle physically the energy. The market regulation establishes the mechanism for including those physical futures in the day-ahead bidding of the Generation Companies. The goal of this work is to optimize coordination between physical futures contracts and the Day-Ahead bidding which follow this regulation. We propose a stochastic quadratic mixed-integer programming model which maximizes the expected profits, taking into account futures contracts settlement. The model gives the simultaneous optimization for the Day-Ahead Market bidding strategy and power planning production (unit commitment) for the thermal units of a price-taker Generation Company. The uncertainty of the day-ahead market price is included in the stochastic model through a set of scenarios. Implementation details and some first computational experiences for small real cases are presented. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Optimization algorithms for electricity market models
Tue, 03/03/2009 - 17:10 — adminIdees:
- Calcular una LB mitjançant LR i passar-li aCPLEX.
Optimal Bidding Strategies for Thermal and Generic Programming Units in the Day-ahead Electricity Market
Fri, 12/19/2008 - 10:57 — admin| Publication Type | Report |
| Year of Publication | 2008 |
| Authors | Heredia, F.-Javier, Rider, Marcos.-J., Corchero, C. |
| Pages | 12 |
| Date | 11/2008 |
| Reference | Research report DR 2008/13, Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. E-Prints UPC, http://hdl.handle.net/2117/2468. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya |
| Prepared for | Published on august 2010 at IEEE Transactions on Power Systems |
| Key Words | research; stochastic programming; electricity markets; day-ahead market, bilateral contracts; Virtual Power Plants; optimal bid |
| Abstract | This paper develops a stochastic programming model that integrates the day-ahead optimal bidding problem with the most recent regulation rules of the Iberian Electricity Market (MIBEL) for bilateral contracts, with a special consideration for the new mechanism to balance the competition of the production market, namely virtual power plants auctions (VPP). The model allows a price-taker generation company to decide the unit commitment of the thermal units, the economic dispatch of the bilateral contracts between the thermal units and the generic programming unit (GPU) and the optimal sale/purchase bids for all units (thermal and generic) observing the MIBEL regulation. The uncertainty of the spot prices is represented through scenario sets built from the most recent real data using scenario reduction techniques. The model was solved with real data from a Spanish generation company and spot prices, and the results are reported and analyzed. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Short- and Medium-Term Multimarket Optimal Electricity Generation Planning with Risk and Environmental Constraints (DPI2008-02153)
Fri, 11/07/2008 - 19:57 — admin| Publication Type | Funded research projects |
| Year of Publication | 2008 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia |
| Type of participation | Project leader |
| Duration | 01/2009-12/2011 |
| Call | Proyectos de Investigación Fundamental no Orientada 2008. IV Plan Nacional de I+D+i (2008-2011) |
| Funding organization | Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Gobierno de España |
| Partners | Unión Fenosa, Gas Natural, Universidad Politècnica de Catalunya, Universidad del País Vasco, Universidade Estadual de Campinas-UNICAMP, University of Edinburgh, Norwegian University of Science and Technology. |
| Full time researchers | 6 EDP |
| Budget | 157.300'00€ |
| Project code | DPI2008-02153 |
| Key Words | research; stochastic programming; electricity markets; risc; multimarket; environmental constraints; project; public; competitive; micinn; energy |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Oferta de treball modelització i optimització de mercats elèctrics
Wed, 04/16/2008 - 13:52 — admin

El Grup d'Optimització Numèrica i Modelització (GNOM) del Departament d'Estadística I Investigació Operativa,
UPC, convoca dues places de tècnic de suport a la recerca. Els candidats seleccionats s'incorporaran al grup de recerca GNOM realitzant tasques de suport a la recerca en modelització i optimització de mercats elèctrics dins del marc del projecte de recerca del Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (DPI2005-09117-C02-01), en col·laboració amb empreses del sector elèctric espanyol i sota la supervisió dels professors Narcís Nabona i F. Javier Heredia.
Second Order Conic Programming
Wed, 04/16/2008 - 10:21 — admin| Publication Type | Conference/School/Seminar attendance |
| Year of Publication | 2008 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia |
| Conference Name | Summer School of the Master on Statistics and Operations Research |
| Event Type | Summer School |
| Conference Organiser | Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research, Technical University of Catalonia |
| Conference Dates | 14-15/04/2008 |
| Conference Location | Barcelona, Spain |
| Abstract | Conic quadratic optimization is an exciting extension of linear optimization. The excitement comes from that many important applications can be modeled as a conic quadratic optimization problem. Moreover, conic quadratic optimization problems can be effciently solved using an appropriate interior-point method. In this course we will review the topic conic quadratic optimization. The review will include basic theory, important applications, algorithms, and available software. Course topics: 1. Basic properties of Second Order Conic Programming (SOCP). Duality 2. Modelling. Important applications. 3. Algorithms for SOCP. 4. Software for SOCP. |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Modelling and Solution of Optimisation Problems
Wed, 10/31/2007 - 10:08 — admin| Publication Type | Conference/School/Seminar attendance |
| Year of Publication | 2004 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia |
| Event Type | Workshop |
| Conference Organiser | Brunel University |
| Conference Dates | 20/06/2004 |
| Conference Location | Uxbridge, U.K. |
| Key Words | AMPL; AMPLStudio; research |
| Abstract | On Sunday 20 June 2004, there will be four parallel workshops on practical optimisation: MPL (Bjarni Kristjansson, Cormac Lucas), AIMMS (Jan Bisschop), AMPL (Robert Fourer, Patrick Valente) and LGO (Janos Pinter). Three of the workshop streams focus on MIP modelling staring with a simple application which is investigated and extended. By the end of the day the participants will not only have been instructed on how to model and solve efficiently their application but they will have been shown how to embed their applications as solutions behind Excel. During the course of the day each session will have case studies presented. The global optimisation workshop will be on applied nonlinear (global and convex) optimisation, with a focus on algorithm and software development and typically will include software demonstrations, as well as a review of engineering, economic, and scientific applications. |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Augmented Lagrangean Relaxation and Decomposition Applied to the Short-Term Hydrothermal Coordination Problem
Mon, 10/29/2007 - 18:36 — admin| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 1999 |
| Authors | Beltran, C.; Heredia, F. J. |
| Conference Name | 19th IFIP TC7 Conference on System Modelling and Optimization |
| Conference Date | 12-16/07/1999 |
| Conference Location | Cambridge, U.K. |
| Type of Work | Contributed oral presentation |
| Key Words | augmented lagrangian relaxation; generalized unit commitment; block coordinated descent method; auxiliary principle problem; research |
| Abstract | The problem dealt with is called the Short-Term Hydrothermal Coordination (SHTC) problem. The objective of this problem is the optimization of electrical production and distribution, considering a short-term planning horizon (from one day to one week). Hydraulic and thermal plants must be coordinated in order to satisfy the customer demand of electricity at the minimum cost and with a reliable service. The model for the STHC problem presented here considers the thermal system, the hydraulic system and the distribution network. Nowadays the Lagrangean Relaxation (LR) method is the most widespread procedure to solve the STHC problem. The initial Classical Lagrangean Relaxation (CLR) method was improved by the Augmented Lagrangean Relaxation (ALR) method, although recent advances in the multiplier updating for the CLR method (cutting plane, bundle methods, etc.) have brought this classical method back into fashion. Two main advantages of the ALR method over the CLR method: (1) the ALR method allows us to obtain a saddle-point even in cases where the CLR method presents a duality gap. The solution of the STHC problem by the CLR method usually yields an infeasible primal solution $x_k$ due to the duality gap, whereas in the ALR method a solution of the dual problem provides a feasible primal solution. (2) The second advantage is that, using the CLR method, the differentiability of the dual function cannot be ensured and therefore nondifferentiable methods must be applied in the CLR method. This difficulty can be overcome if an augmented Lagrangean is used, since the dual function $q_c$ is differentiable for an appropriate c. Thus, the multipliers can be updated using ``large steps''. The main weakness of the ALR method is that the quadratic terms introduced by the augmented Lagrangean are not separable. If we want to solve the STHC problem by decomposition, some methods, such as the Auxiliary Problem Principle, or, as in our case, the Block Coordinate Descent method, must be used. However, the CLR method gives a separable Lagrangean. The starting point is the paper by Batut and Renaud [1] and therefore we use Variable Duplication plus the Augmented Lagrangean Relaxation (ALR) method. The method used by Batut and Renaud is improved theoretically and practically. From the theoretical point of view, the conservative Auxiliary Problem Principle is replaced by the Block Coordinate Descent Method that shows to be faster. From the practical point of view, an effective software package designed to solve the Optimum Short-Term Hydrothermal Coordination Problem, is incorporated in order to speed up the whole algorithm. Several medium to large scale instances of this problem have been solved showing the applicability of the proposed procedure. |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
