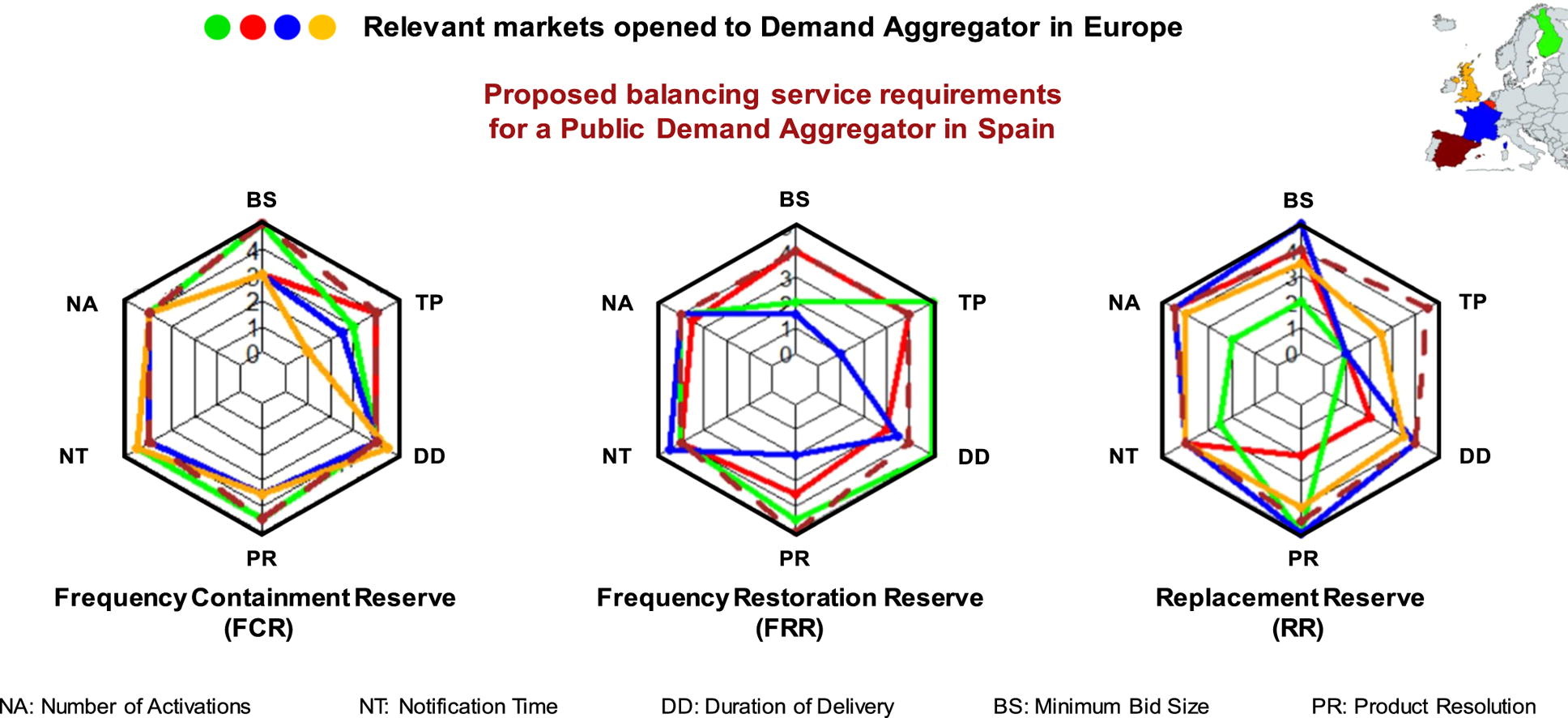
 The paper entittled Critical evaluation of European balancing markets to enable the participation of Demand Aggregators has been published in Applied Energy This paper has been done in collaboration with the Institute for Energy Research of Catalonia (IREC). This study analyzes barriers and enablers of four European electricity markets and proposes a new market framework that would enhance Demand Aggregators' participation. Main barriers for Demand Aggregators have been identified and analyzed and a regulation scheme is proposed to enable Demand Aggregators participation. According to our results, small tertiary building aggregation is still not economic viable but existing municipal retailers could consider to extend their operations to Demand Aggregation.
The paper entittled Critical evaluation of European balancing markets to enable the participation of Demand Aggregators has been published in Applied Energy This paper has been done in collaboration with the Institute for Energy Research of Catalonia (IREC). This study analyzes barriers and enablers of four European electricity markets and proposes a new market framework that would enhance Demand Aggregators' participation. Main barriers for Demand Aggregators have been identified and analyzed and a regulation scheme is proposed to enable Demand Aggregators participation. According to our results, small tertiary building aggregation is still not economic viable but existing municipal retailers could consider to extend their operations to Demand Aggregation.

 The MSc Thesis entitled
The MSc Thesis entitled