energy and power systems
Unified multi-market participation of energy communities in energy markets (OptiREC)
Tue, 01/17/2023 - 20:34 — admin| Publication Type | Funded research projects |
| Year of Publication | 2022 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Albert Solà Vilalta; Marlyn Dayana Cuadrado Guevara |
| Type of participation | Leader |
| Duration | 01/23-12/24 |
| Call | PROYECTOS DE TRANSICIÓN ECOLÓGICA Y TRANSICIÓN DIGITAL 2021 |
| Funding organization | MINISTERIO DE CIENCIA E INNOVACIÓN |
| Partners | IREC, Universitat de Girona, Universidad Comillas. |
| Full time researchers | 2,5 |
| Budget | 149.500€ |
| Project code | TED2021-131365B-C44 |
| Key Words | research; TED2021-131365B-C44; energy communities; electricity markets; bilevel stochastic programming |
| Abstract | The general purpose of this subproject is to study the participation of energy communities in the multimarket structure of the wholesale electricity market in order to develop mathematical models and computational tools for the optimal bid to wholesale markets. From the point of view of the wholesale electricity market, all the complexity of the inner structure of energy communities (dispatchable and nondispatchable generation, storage, demand,) can be conceptually understood as a single virtual programming unit ( a Community Virtual Programming Unit, CVPU) that participate in the wholesale electricity multimarket structure (spot and ancillary-services markets). The final goal of this project is to develop a multi-stage stochastic-programming model for the Multimarket Optimal Bid of Energy Communities (MOBEC) problem that will be validated with real data from the Iberian Electricity Market (MIBEL). Conceptually speaking, energy communities are a complex energy system comprising dispatchable and non-dispatchable generation, energy storage systems and an own demand, that participate in the wholesale electricity market. Based on the experience of previous studies the extension of stochastic programming models to energy communities is a fairly natural and a sounded research methodology. First, the participation of energy communities in spot markets will be analysed. Spot markets (day and intraday) are the most important one in terms of the amount of energy traded. A CVPU will be defined allowing the energy community to submit bids to the single day ahead and to the multiple intraday markets, according to the MIBEL rules. Second, the participation of energy communities in ancillary services markets will be studied. Dispatchable generation units (thermal) together with storage devices and demand flexibility provide the energy community with reserve capabilities that can be bid to the secondary reserve market. The reserve of the CVPU will be defined, formulated and integrated in the (MOBEC) optimization model. The resulting model will be implemented and validated with real data from the real energy communities and the MIBEL. Multi-stage stochastic programming optimal bid models have been successfully developed so far for generation+storage units and will be extended in this project and adapted to the specific features of an energy community through a CVPU that participates in the wholesale electricity market as a single programming unit. |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Presentation at the EURO 2022 conference in Finland.
Fri, 07/08/2022 - 12:10 — admin
Ph D. Thesis on multistage scenario tree generation for renewable energies.
Mon, 11/30/2020 - 19:40 — admin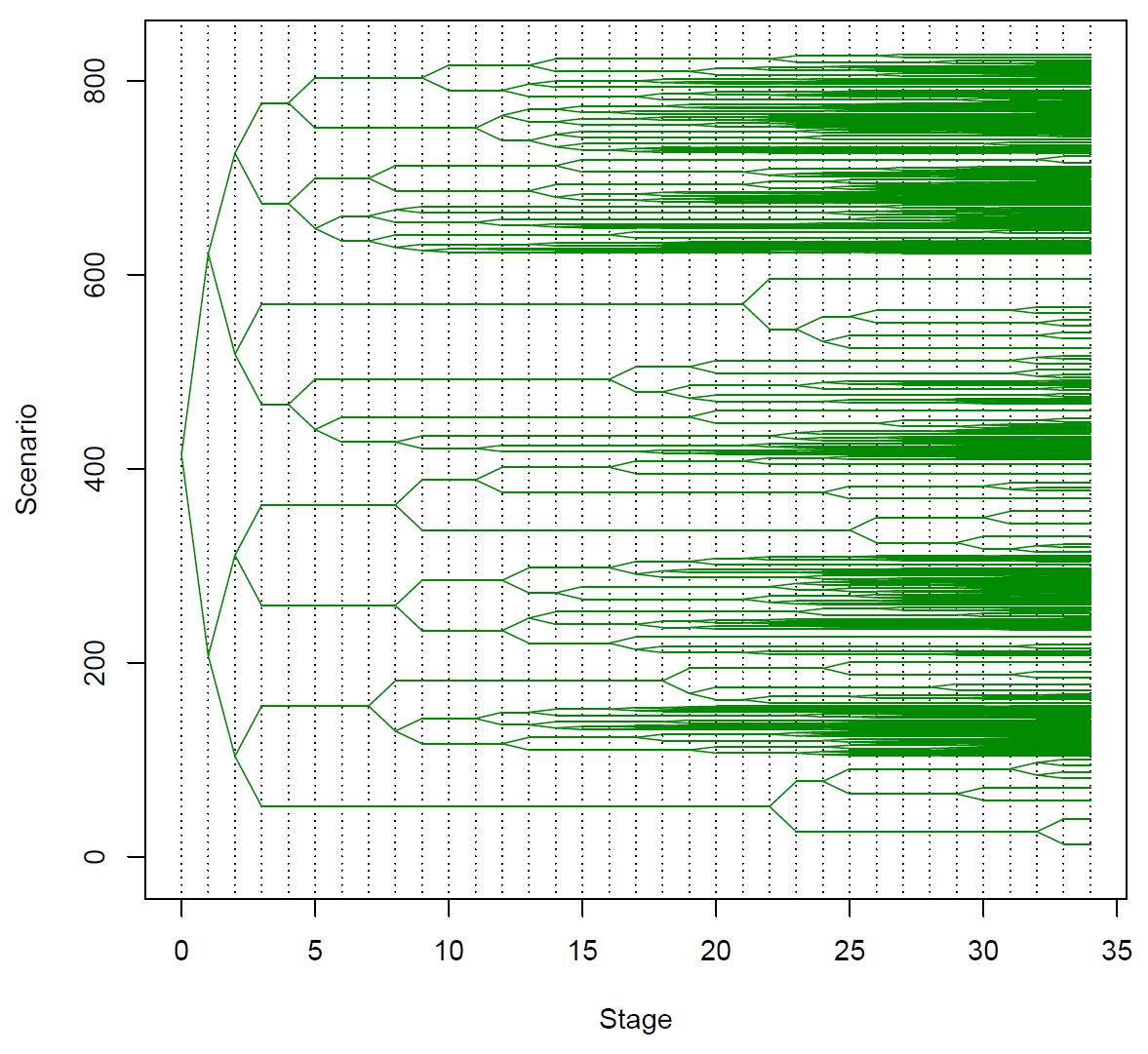 On November 30th 2020 took place the defense of the Ph.D. Thesis entittled "Multistage Scenario Trees Generation for Renewable Energy Systems Optimization", authored by Ms. Marlyn D. Cuadrado Guevara and advised by prof. F.-Javier Heredia. In this thesis a new methodology to generate and validate probability scenario trees for multistage stochastic programming problems arising in two different energy systems with renewables are proposed. The first problem corresponds to the optimal bid to electricity markets of a virtual power plant that consists on a wind-power plant plus a battery storage energy systems. The second one is the optimal operation of a distribution grid with some photovoltaic production.
On November 30th 2020 took place the defense of the Ph.D. Thesis entittled "Multistage Scenario Trees Generation for Renewable Energy Systems Optimization", authored by Ms. Marlyn D. Cuadrado Guevara and advised by prof. F.-Javier Heredia. In this thesis a new methodology to generate and validate probability scenario trees for multistage stochastic programming problems arising in two different energy systems with renewables are proposed. The first problem corresponds to the optimal bid to electricity markets of a virtual power plant that consists on a wind-power plant plus a battery storage energy systems. The second one is the optimal operation of a distribution grid with some photovoltaic production.
Multistage Scenario Trees Generation for Renewable Energy Systems Optimization
Mon, 11/30/2020 - 19:17 — admin| Publication Type | Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2020 |
| Authors | Marlyn Dayana Cuadrado Guevara |
| Academic Department | Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. Prof. F.-Javier Heredia, advisor. |
| Number of Pages | 194 |
| University | Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya-BarcelonaTech |
| City | Barcelona |
| Degree | PhD Thesis |
| Key Words | research; Battery energy storage systems; Electricity markets; Ancillary services market; Wind power generation; Virtual power plants; Multistage Stochastic programming; phd thesis |
| Abstract | The presence of renewables in energy systems optimization have generated a high level of uncertainty in the data, which has led to a need for applying stochastic optimization to modelling problems with this characteristic. The method followed in this thesis is Multistage Stochastic Programming (MSP). Central to MSP is the idea of representing uncertainty (which, in this case, is modelled with a stochastic process) using scenario trees. In this thesis, we developed a methodology that starts with available historical data; generates a set of scenarios for each random variable of the MSP model; defines individual scenarios that are used to build the initial stochastic process (as a fan or an initial scenario tree); and builds the final scenario trees that are the approximation of the stochastic process. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
New paper published in Applied Energy
Fri, 04/03/2020 - 12:05 — admin
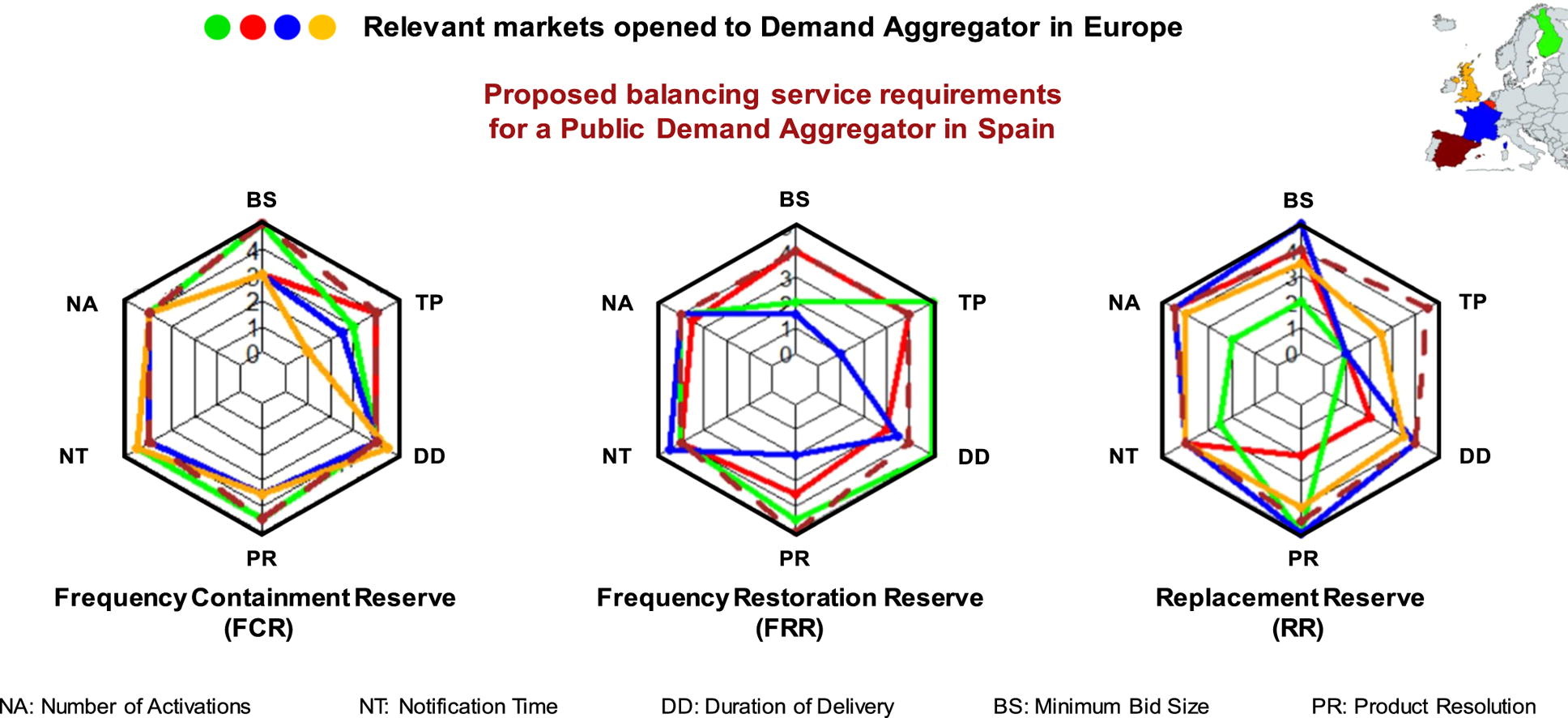 The paper entittled Critical evaluation of European balancing markets to enable the participation of Demand Aggregators has been published in Applied Energy This paper has been done in collaboration with the Institute for Energy Research of Catalonia (IREC). This study analyzes barriers and enablers of four European electricity markets and proposes a new market framework that would enhance Demand Aggregators' participation. Main barriers for Demand Aggregators have been identified and analyzed and a regulation scheme is proposed to enable Demand Aggregators participation. According to our results, small tertiary building aggregation is still not economic viable but existing municipal retailers could consider to extend their operations to Demand Aggregation.
The paper entittled Critical evaluation of European balancing markets to enable the participation of Demand Aggregators has been published in Applied Energy This paper has been done in collaboration with the Institute for Energy Research of Catalonia (IREC). This study analyzes barriers and enablers of four European electricity markets and proposes a new market framework that would enhance Demand Aggregators' participation. Main barriers for Demand Aggregators have been identified and analyzed and a regulation scheme is proposed to enable Demand Aggregators participation. According to our results, small tertiary building aggregation is still not economic viable but existing municipal retailers could consider to extend their operations to Demand Aggregation.
Critical evaluation of European balancing markets to enable the participation of Demand Aggregators
Fri, 04/03/2020 - 11:42 — admin| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2020 |
| Authors | Mattia Barbero; Cristina Corchero; Lluc Canals; Lucia Igualada; F.-Javier Heredia |
| Journal Title | Applied Energy |
| Volume | 264 |
| Journal Date | 04/2020 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| ISSN Number | 0306-2619/ |
| Key Words | Demand Aggregator; Regulatory framework; Ancillary Services; Demand Response; Tertiary building management; research; paper |
| Abstract | European Directives are incentivizing consumers to play an active role in the electricity system and to collaborate to maintain its stability, which has been historically provided by large generation power plants. However, it is not easy for the System Operator to handle the coexistence of consumers and generators in the same markets. Under these circumstances, a new actor allows small residential and commercial consumers to participate in flexibility markets: The Demand Aggregator. However, balancing markets opened to Demand Aggregators still present several barriers that do not allow their practical participation. This study analyzes barriers and enablers of four European electricity markets and proposes a new market framework that would enhance Demand Aggregators’ participation. To validate the proposed market and to understand the economic potentials of aggregated small tertiary buildings, a Demand Aggregator is simulated using real building’s consumption data. Results show that technical requirements to participate in balancing markets such as the minimum bid size, the symmetricity of the offer and the product resolution strongly affect incomes for Demand Aggregators. However, neither in the proposed market, the creation of a Demand Aggregator whose business model is focused on small tertiary buildings does not seem realistic due to low incomes in comparison to the fixed costs necessary to enable Demand Response, especially if only the air conditioning system is considered. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114707 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
A MIP formulation of a Hybrid AC-DC offshore wind power plant topology
Wed, 07/11/2018 - 11:26 — admin| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 2018 |
| Authors | Cristina Corchero; Josep Homs-Moreno; F.-Javier Heredia; Lucia Igualada; Mikel de Prada |
| Conference Name | 23th International Symposium on Mathematical Programming |
| Conference Date | 01-06/07/2018 |
| Conference Location | Bordeaux |
| Type of Work | contributed presentation |
| Key Words | research; hybrid AC-DC; offshore wind power plant; local branching |
| Abstract | The current study analyses a hybrid o↵shore wind farm design in which individual wind turbine power converters are removed from wind turbines and are installed on intermediate o↵shore collector platforms. In this study a compact and small-sized mixedinteger linear optimisation model makes four decisions with the goal of minimising installation and operation costs: the location and the number of o↵shore platforms and power converters to be installed, the optimal wind farm cable layout and the cluster optimal operating frequency of each wind turbine. The solutions found either for small and large o↵shore wind farms improve notoriously real-world designs, reducing up to 8 percent installation and maintenance costs. On the optimization technical results, a variant of Local Branching has been developed, reducing in some cases more than half of computing time with respect to default Local Branching. The model developed serves as a mathematical tool to provide rigorous evidences of the suitability of the hybrid design versus traditional o↵shore wind farm designs. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
A multistage stochastic programming model for the optimal bid of a wind producer
Wed, 07/11/2018 - 11:20 — admin| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 2018 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Marlyn D. Cuadrado; J.-Anton Sánchez |
| Conference Name | 23th International Symposium on Mathematical Programming |
| Conference Date | 01-06/07/2018 |
| Conference Location | Bordeaux |
| Type of Work | contributed presentation |
| Key Words | research; Battery energy storage systems; Electricity markets; Ancillary services market; Wind power generation; Virtual power plants; Stochastic programming |
| Abstract | Abstract: Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) can be used by wind producers to improve the operation of wind power plants (WPP) in electricity markets. Associating a wind power plant with a BESS (the so-called Virtual Power Plant (VPP)) provides utilities with a tool that converts uncertain wind power production into a dispatchable technology that can operate not only in spot and adjustment markets (day-ahead and intraday markets) but also in ancillary services markets that, up to now, were forbidden to non-dispatchable technologies. We present in this study a multi-stage stochastic programming model to find the optimal operation of a VPP in the day-ahead, intraday and secondary reserve markets while taking into account uncertainty in wind power generation and clearing prices (day-ahead, secondary reserve, intraday markets and system imbalances). A new forecasting procedure for the random variables involved in stochastic programming model has been developed. The forecasting model is based on Time Factor Series Analysis (TFSA) and gives suitable results while reducing the dimensionality of the forecasting mode. The quality of the scenario trees generated using the TFSA forecasting models with real electricity markets and wind production data has been analysed through multistage VSS. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
On optimal participation in the electricity markets of wind power plants with battery energy storage systems
Tue, 05/15/2018 - 16:25 — admin| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2018 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Marlyn D. Cuadrado; Cristina Corchero |
| Journal Title | Computers and Operations Research |
| Volume | 96 |
| Pages | 316-329 |
| Journal Date | 08/2018 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| ISSN Number | 0305-0548 |
| Key Words | research; Battery energy storage systems; Electricity markets; Ancillary services market; Wind power generation; Virtual power plants; Stochastic programming; paper |
| Abstract | The recent cost reduction and technological advances in medium- to large-scale battery energy storage systems (BESS) makes these devices a true alternative for wind producers operating in electricity markets. Associating a wind power farm with a BESS (the so-called virtual power plant (VPP)) provides utilities with a tool that converts uncertain wind power production into a dispatchable technology that can operate not only in spot and adjustment markets (day-ahead and intraday markets) but also in ancillary services markets that, up to now, were forbidden to non-dispatchable technologies. What is more, recent studies have shown capital cost investment in BESS can be recovered only by means of such a VPP participating in the ancillary services markets. We present in this study a multi-stage stochastic programming model to find the optimal operation of a VPP in the day-ahead, intraday and secondary reserve markets while taking into account uncertainty in wind power generation and clearing prices (day-ahead, secondary reserve, intraday markets and system imbalances). A case study with real data from the Iberian electricity market is presented. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.cor.2018.03.004 |
| Preprint | http://hdl.handle.net/2117/118479 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Stochastic optimal generation bid to electricity markets with emissions risk constraints.
Tue, 01/30/2018 - 21:12 — admin| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2018 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Julián Cifuentes-Rubiano; Cristina Corchero |
| Journal Title | Journal of Environmental Management |
| Volume | 207 |
| Issue | 1 |
| Pages | 12 |
| Start Page | 432 |
| Journal Date | February 2018 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| ISSN Number | 0301-4797 |
| Key Words | research; OR in Energy; Stochastic Programming; Risk Management; Electricity market; Emissions reduction; paper |
| Abstract | There are many factors that influence the day-ahead market bidding strategies of a generation company (GenCo) within the framework of the current energy market. Environmental policy issues are giving rise to emission limitation that are becoming more and more important for fossil-fueled power plants, and these must be considered in their management. This work investigates the influence of the emissions reduction plan and the incorporation of the medium-term derivative commitments in the optimal generation bidding strategy for the day-ahead electricity market. Two different technologies have been considered: the high-emission technology of thermal coal units and the low-emission technology of combined cycle gas turbine units. The Iberian Electricity Market (MIBEL) and the Spanish National Emissions Reduction Plan (NERP) defines the environmental framework for dealing with the day-ahead market bidding strategies. To address emission limitations, we have extended some of the standard risk management methodologies developed for financial markets, such as Value-at-Risk (VaR) and Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR), thus leading to the new concept of Conditional Emission at Risk (CEaR). This study offers electricity generation utilities a mathematical model for determining the unit’s optimal generation bid to the wholesale electricity market such that it maximizes the long-term profits of the utility while allowing it to abide by the Iberian Electricity Market rules as well as the environmental restrictions set by the Spanish National Emissions Reduction Plan. We analyze the economic implications for a GenCo that includes the environmental restrictions of this National Plan as well as the NERP’s effects on the expected profits and the optimal generation bid. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.010 |
| Preprint | http://hdl.handle.net/2117/114024 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
