bilateral contracts
Fri, 07/08/2022 - 12:10 — admin

Last July 4 2022 I was invited at the EURO 2022 conference , Aalto University, Espoo, near Helsinki, to present the work Multistage stochastic programming for the optimal bid of a wind-thermal power production pool with battery storage, which is a continuation of the MSc and PhD thesis of Mr. Ignasi Manyé and Ms. Marlyn D. Cuadrado respectively. This work tackles with an extensive study along a complete timespan of on year analyzing the benefits of a joint operation of a wind and thermal generation system in the elecrticity markets and bilateral contracts. Numerical results show that the total profit increases by 13% in average, but that it can be as high as 77%, with a reduction of the thermal operation costs of 61%.
Fri, 07/08/2022 - 11:26 — admin
| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 2022 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Ignasi Mañé; Marlyn Dayana Cuadrado Guevara |
| Conference Name | EURO 2022 |
| Conference Date | 03-06/07/2022 |
| Conference Location | Espoo, Finland. |
| Type of Work | Invited presentation |
| ISBN Number | 978-951-95254-1-9 |
| Key Words | research; multistage stochastic programming; virtual power plants; unit commitment |
| Abstract | In this study we present a multistage stochastic programming model to find the joint optimal bid to electricity markets of a pool of dispatchable (thermal) and non-dispatchable (wind) production units with battery storage facilities. The assumption is that these programming units are operated by the same utility that, previous to the market clearing, has to dispatch some bilateral contracts with the joint production of the production pool. The multistage model mimics the multimarket bidding process in the Iberian Electricity Market (MIBEL). First, the utility has to decide how to cover the energy of the bilateral contracts with the available units. Second, the production capacity of each unit, not allocated to the bilateral contracts, must be offered to the seven consecutives spot markets (day-ahead and six intraday markets) plus the secondary reserve market (the most relevant ancillary services market). The stochasticity of the electricity clearing prices and the hourly generation of the wind-power units is considered. The stochastic process associated to this multistage decision-making process is modelled through multistage scenario trees with thirty-four stages that are built from forecasting models based on real data of the Iberian Electricity Market. The numerical results show the advantage of the joint operation of the pool of production units with an increase of the overall expected profits, mainly due to a strong reduction of the operational costs. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 12/30/2021 - 13:20 — admin
| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2021 |
| Authors | Ignasi Mañé Bosch |
| Director | F-Javier Heredia |
| Tipus de tesi | MSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Master in Statistics and Operations Reseafrch |
| Centre | Facultat de matemàtiques i Estadística |
| Data defensa | 18/10/2021 |
| Nota // mark | 9.5 |
| Key Words | teaching; electricity markets; multistage stochastic programming |
| Abstract | For many political and economic reasons, over the last decades, electricity markets in developed countries have been liberalised. Markets regulated by governments in which prices were set by the competent authority are now the exception. In this new setting, electricity agents, both consumers and producers, compete to maximise their pro�tability in a series of auctions designed to efficiently match supply and demand. Many energy producers manage together wind and thermal generation units to meet their contractual obligations such as bilateral contracts, as well as bid on the electric market to sell their production capacity. This master thesis explore different multi-stage stochastic programming models for generation companies to �nd optimal bid functions in electric spot markets. The explored models not only capture the uncertainty of electric prices of different markets and
�financial products, but also couples together wind and thermal generation units, offering producers that combine both technologies a more suitable approach to �nd their best possible bidding strategy among the space of possible actions. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Wed, 12/01/2021 - 13:35 — admin
On November 2021 Mr. Ignasi Mañé presented the MsC thesis dissertation Multistage stochastic bid model for a wind-thermal power producer to opt for the master's degree in Statistics and Operations Research (UPC-UB), advised by prof. F.-Javier Heredia. This master thesis explores different multi-stage stochastic programming models for generation companies to find optimal bid functions in electric spot markets capturing the uncertainty of electric prices of different markets and financial products, and coupling together wind and thermal generation unit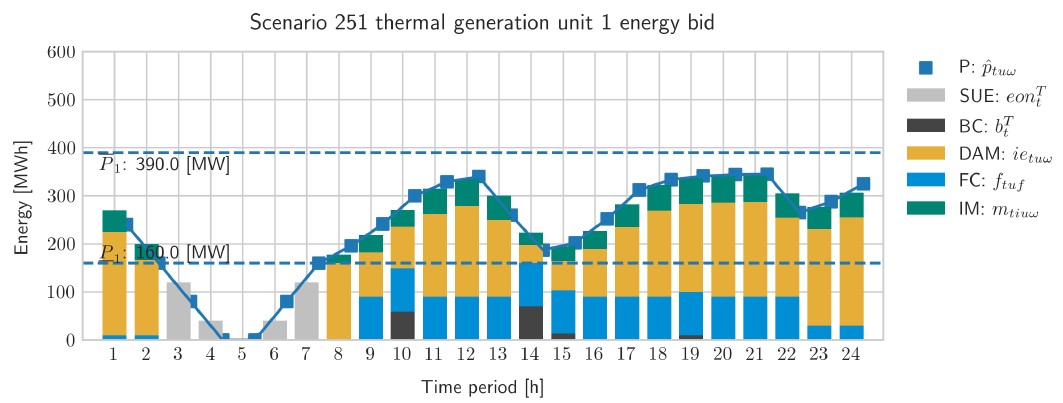
Tue, 01/30/2018 - 21:12 — admin
| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2018 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Julián Cifuentes-Rubiano; Cristina Corchero |
| Journal Title | Journal of Environmental Management |
| Volume | 207 |
| Issue | 1 |
| Pages | 12 |
| Start Page | 432 |
| Journal Date | February 2018 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| ISSN Number | 0301-4797 |
| Key Words | research; OR in Energy; Stochastic Programming; Risk Management; Electricity market; Emissions reduction; paper |
| Abstract | There are many factors that influence the day-ahead market bidding strategies of a generation company (GenCo) within the framework of the current energy market. Environmental policy issues are giving rise to emission limitation that are becoming more and more important for fossil-fueled power plants, and these must be considered in their management. This work investigates the influence of the emissions reduction plan and the incorporation of the medium-term derivative commitments in the optimal generation bidding strategy for the day-ahead electricity market. Two different technologies have been considered: the high-emission technology of thermal coal units and the low-emission technology of combined cycle gas turbine units. The Iberian Electricity Market (MIBEL) and the Spanish National Emissions Reduction Plan (NERP) defines the environmental framework for dealing with the day-ahead market bidding strategies. To address emission limitations, we have extended some of the standard risk management methodologies developed for financial markets, such as Value-at-Risk (VaR) and Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR), thus leading to the new concept of Conditional Emission at Risk (CEaR). This study offers electricity generation utilities a mathematical model for determining the unit’s optimal generation bid to the wholesale electricity market such that it maximizes the long-term profits of the utility while allowing it to abide by the Iberian Electricity Market rules as well as the environmental restrictions set by the Spanish National Emissions Reduction Plan. We analyze the economic implications for a GenCo that includes the environmental restrictions of this National Plan as well as the NERP’s effects on the expected profits and the optimal generation bid. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.010 |
| Preprint | http://hdl.handle.net/2117/114024 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Fri, 07/17/2015 - 13:02 — admin
| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 2015 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Antonio Rengifo |
| Conference Name | 27th European Conference on Operational Research |
| Conference Date | 12-15/07/2015 |
| Conference Location | Glasgow, UK. |
| Type of Work | invited |
| Key Words | research; MTM2013-48462-C2-1; mixed-integer nonlinear programming; proximal bundle methods; multimarket electricity problems; parallelism |
| Abstract | The use of stochastic programming to solve real instances of optimal bid problems in electricity market usually implies the solution of large scale mixed integer nonlinear optimization problems that can't be tackled with the available general purpose commercial optimisation software. In this work we show the potential of proximal bundle methods to solve large scale stochastic programming problems arising in electricity markets. Proximal bundle methods was used in the past to solve deterministic unit commitment problems and are extended in this work to solve real instances of stochastic optimal bid problems to the day-ahead market (with embedded unit commitment) with thousands of scenarios. A parallel implementation of the proximal bundle method has been developed to take profit of the separability of the lagrangean problem in as many subproblems as generation bid units. The parallel proximal bundle method (PPBM) is compared against general purpose commercial optimization software as well as against the perspective cuts algorithm, a method specially conceived to deal with quadratic objective function over semi-continuous domains. The reported numerical results obtained with a workstation with 32 threads show that the commercial software can’t find a solution beyond 50 scenarios and that the execution times of the proposed PPBM are as low as a 15% of the execution time of the perspective cut approach for problems beyond 800 scenarios.
|
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 11/27/2014 - 21:20 — admin
| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 2014 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Julián Cifuentes; Cristina Corchero |
| Conference Name | IFORS2014: 20th Conference of the International Federation of Operational Research Societies |
| Conference Date | 13-18/07/2014 |
| Conference Location | Barcelona |
| Type of Work | Invited presentation |
| Key Words | research; emission limits; risk; stochastic programming; day-ahead electricity market; combined cycle units |
| Abstract | This work allows investigating the influence of the emission reduction plan, and the incorporation of the derivatives medium-term commitments in the optimal generation bidding strategy to the day-ahead electricity market. Two different technologies have been considered: the coal thermal units, high-emission technology, and the combined cycle gas turbine units, low-emission technology. The Iberian Electricity Market (MIBEL) and the Spanish National Emission Reduction Plan (NERP) defines the environmental framework to deal with by the day-ahead market bidding strategies. To address emission limitations, some of the standard risk management methodologies developed for financial markets, such as Value-at-Risk (VaR) and Conditional Valueat-
Risk (CVaR), have been extended giving rise to the new concept of Conditional Emission at Risk (CEaR). The economic implications for a GenCo of including the environmental restrictions of this National Plan are analyzed, and the effect of the NERP in the expected profits and optimal generation bid are analyzed. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Sun, 11/17/2013 - 19:22 — admin
| Publication Type | Report |
| Year of Publication | 2013 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Julian Cifuentes; Cristina Corchero |
| Pages | 21 |
| Date | 09/2013 |
| Reference | Research report DR 2013/04, Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. E-Prints UPC, http://hdl.handle.net/2117/20640. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya |
| Prepared for | submitted |
| Key Words | research; OR in Energy; Stochastic Programming; Risk Management; Electricity market; Emission reduction |
| Abstract | There are many factors that influence the day-ahead market bidding strategies of a generation company (GenCo) in the current energy market framework. Environmental policy issues have become more and more important for fossil-fuelled power plants and they have to be considered in their management, giving rise to emission limitations. This work allows investigating the influence of the emission reduction plan, and the incorporation of the derivatives medium-term commitments in the optimal generation bidding strategy to the day-ahead electricity market. Two different technologies have been considered: the coal thermal units, high-emission technology, and the combined
cycle gas turbine units, low-emission technology. The Iberian Electricity Market (MIBEL) and the Spanish National Emission Reduction Plan (NERP) defines the environmental framework to deal with by the day-ahead market bidding strategies. To address emission limitations, some of the standard risk management methodologies
developed for financial markets, such as Value-at-Risk (VaR) and Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR), have been extended giving rise to the new concept of Conditional Emission-at-Risk (CEaR). This study offers to electricity generation utilities a mathematical model to determinate the individual optimal generation bid to the wholesale
electricity market, for each one of their generation units that maximizes the long-run profits of the utility abiding by the Iberian Electricity Market rules, as well as the environmental restrictions set by the Spanish National Emissions Reduction Plan. The economic implications for a GenCo of including the environmental restrictions of this
National Plan are analyzed, and the effect of the NERP in the expected profits and optimal generation bid are analyzed. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Fri, 09/06/2013 - 15:58 — admin
| Publication Type | Report |
| Year of Publication | 2011 |
| Authors | Cristina Corchero; Eugenio Mijangos; F.-Javier Heredia |
| Pages | 25 |
| Date | 11/2011 |
| Reference | Research report DR 2011/04, Dept. of Statistics and Operations Research. E-Prints UPC, http://hdl.handle.net/2117/18368. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya |
| Prepared for | Published by TOP |
| Key Words | research; electricity market; |
| Abstract | On current electricity markets the electrical utilities are faced with very sophisticated
decision making problems under uncertainty. Moreover, when focusing in the shortterm
management, generation companies must include some medium-term products that
directly influence their short-term strategies. In this work, the bilateral and physical futures
contracts are included into the day-ahead market bid following MIBEL rules and a stochastic
quadratic mixed-integer programming model is presented. The complexity of this stochastic
programming problem makes unpractical the resolution of large-scale instances with general purpose optimization codes. Therefore, in order to gain efficiency, a polyhedral outer approximation of the quadratic objective function obtained by means of perspective cuts (PC) is proposed. A set of instances of the problem has been defined with real data and solved with the PC methodology. The numerical results obtained show the efficiency of this methodology compared with standard mixed quadratic optimization solvers. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 07/19/2012 - 20:45 — admin
| Publication Type | Proceedings Article |
| Year of Publication | 2012 |
| Authors | Cristina Corchero; F.-Javier Heredia; Julián Cifuentes |
| Conference Name | 2012 9th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM 2012) |
| Series Title | IEEE Conference Publications |
| Pagination | 1-8 |
| Conference Start Date | 10/05/2012 |
| Publisher | IEEE |
| Conference Location | Florence |
| Editor | IEEE |
| ISSN Number | - |
| ISBN Number | 978-1-4673-0834-2 |
| Key Words | research; elecriticy; markets; CO2 allowances; emissions limits; environment; stochastic programming; modeling languages; paper |
| Abstract | There are many factors that influence the day-ahead market bidding strategies of a GenCo in the current energy
market framework. In this work we study the influence of both the allowances and emission reduction plan and the incorporation of the derivatives medium-term commitments in the optimal generation bidding strategy to the day-ahead electricity market. Two different technologies have been considered: the coal thermal units, high-emission technology, and the combined cycle gas turbine units, low-emission technology. The operational characteristics of both kinds of units are modeled in detail. We deal with this problem in the framework of the Iberian Electricity Market and the Spanish National Emissions and Allocation Plans. The economic implications for a GenCo of including the environmental restrictions of these National Plans are analyzed. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | 10.1109/EEM.2012.6254676 |
| Preprint | http://hdl.handle.net/2117/18691 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |

|


