research
Thu, 10/24/2024 - 11:48 — admin
| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 2024 |
| Authors | Albert Solà Vilalta, Marlyn Cuadrado, Ignasi Mañé, F.-Javier Heredia |
| Conference Name | ISMP2024, 25th International Symposium on Mathematical Programming |
| Conference Date | 21-26/07/2024 |
| Conference Location | Montréal, Canada. |
| Type of Work | Invited presentation |
| Key Words | energy communities; electricity markets; demand flexibility; prosumers; mathematical optimization; stochastic programming; research |
| Abstract | An energy community is a legal figure, recently coined by the European Union, that creates a framework to encourage active participation of citizens and local entities in the energy transition to net-zero. In this work, we study the optimal participation of energy communities in day-ahead, reserve, and intraday electricity markets. where energy communities cannot meet their internal demand, and periods where they generate excess electricity. This is because the electricity they generate often comes from variable renewable resources like solar and wind. Electricity market participation is a natural way to ensure they meet their internal demand at all times, and, simultaneously, make the most of the excess electricity. We propose a multi-stage stochastic programming model that captures variable renewable and electricity price uncertainty. The multi-stage aspect models the di¿erent times at which variable renewable generation is considered to be known and electricity prices from di¿erent markets are revealed. This results in a very large scenario tree with 34 stages, and hence a very large optimization problem. Scenario reduction techniques are applied to make the problem tractable. Case studies with real data are discussed, considering di¿erent energy community configurations, to analyse proposed regulatory frameworks in Europe. The added value of considering stochasticity in this problem is also analysed. The motivation to do so is that there are time periods |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Mon, 06/17/2024 - 18:57 — admin
Tue, 01/17/2023 - 20:34 — admin
| Publication Type | Funded research projects |
| Year of Publication | 2022 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Albert Solà Vilalta; Marlyn Dayana Cuadrado Guevara |
| Type of participation | Leader |
| Duration | 01/23-12/24 |
| Call | PROYECTOS DE TRANSICIÓN ECOLÓGICA Y TRANSICIÓN DIGITAL 2021 |
| Funding organization | MINISTERIO DE CIENCIA E INNOVACIÓN |
| Partners | IREC, Universitat de Girona, Universidad Comillas. |
| Full time researchers | 2,5 |
| Budget | 149.500€ |
| Project code | TED2021-131365B-C44 |
| Key Words | research; TED2021-131365B-C44; energy communities; electricity markets; bilevel stochastic programming |
| Abstract | The general purpose of this subproject is to study the participation of energy communities in the multimarket structure of the wholesale electricity market in order to develop mathematical models and computational tools for the optimal bid to wholesale markets. From the point of view of the wholesale electricity market, all the complexity of the inner structure of energy communities (dispatchable and nondispatchable generation, storage, demand,) can be conceptually understood as a single virtual programming unit ( a Community Virtual Programming Unit, CVPU) that participate in the wholesale electricity multimarket structure (spot and ancillary-services markets). The final goal of this project is to develop a multi-stage stochastic-programming model for the Multimarket Optimal Bid of Energy Communities (MOBEC) problem that will be validated with real data from the Iberian Electricity Market (MIBEL). Conceptually speaking, energy communities are a complex energy system comprising dispatchable and non-dispatchable generation, energy storage systems and an own demand, that participate in the wholesale electricity market. Based on the experience of previous studies the extension of stochastic
programming models to energy communities is a fairly natural and a sounded research methodology. First, the participation of energy communities in spot markets will be analysed. Spot markets (day and intraday) are the most important one in terms of the amount of energy traded. A CVPU will be defined allowing the energy community to submit bids to the single day ahead and to the multiple intraday markets, according to the MIBEL rules. Second, the participation of energy communities in ancillary services markets will be studied. Dispatchable generation units (thermal) together with storage devices and demand flexibility provide the energy community with reserve capabilities that can be bid to the secondary reserve market. The reserve of the CVPU will be defined, formulated and integrated in the (MOBEC) optimization model. The resulting model will be implemented and validated with real data from the real energy communities and the MIBEL. Multi-stage stochastic programming optimal bid models have been successfully developed so far for generation+storage units and will be extended in this project and adapted to the specific features of
an energy community through a CVPU that participates in the wholesale electricity market as a single programming unit. |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Thu, 12/30/2021 - 13:20 — admin
| Publication Type | Tesis de Grau i Màster // BSc and MSc Thesis |
| Year of Publication | 2021 |
| Authors | Ignasi Mañé Bosch |
| Director | F-Javier Heredia |
| Tipus de tesi | MSc Thesis |
| Titulació | Master in Statistics and Operations Reseafrch |
| Centre | Facultat de matemàtiques i Estadística |
| Data defensa | 18/10/2021 |
| Nota // mark | 9.5 |
| Key Words | teaching; electricity markets; multistage stochastic programming |
| Abstract | For many political and economic reasons, over the last decades, electricity markets in developed countries have been liberalised. Markets regulated by governments in which prices were set by the competent authority are now the exception. In this new setting, electricity agents, both consumers and producers, compete to maximise their pro�tability in a series of auctions designed to efficiently match supply and demand. Many energy producers manage together wind and thermal generation units to meet their contractual obligations such as bilateral contracts, as well as bid on the electric market to sell their production capacity. This master thesis explore different multi-stage stochastic programming models for generation companies to �nd optimal bid functions in electric spot markets. The explored models not only capture the uncertainty of electric prices of different markets and
�financial products, but also couples together wind and thermal generation units, offering producers that combine both technologies a more suitable approach to �nd their best possible bidding strategy among the space of possible actions. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Tue, 07/13/2021 - 11:24 — admin
Mon, 11/30/2020 - 19:40 — admin
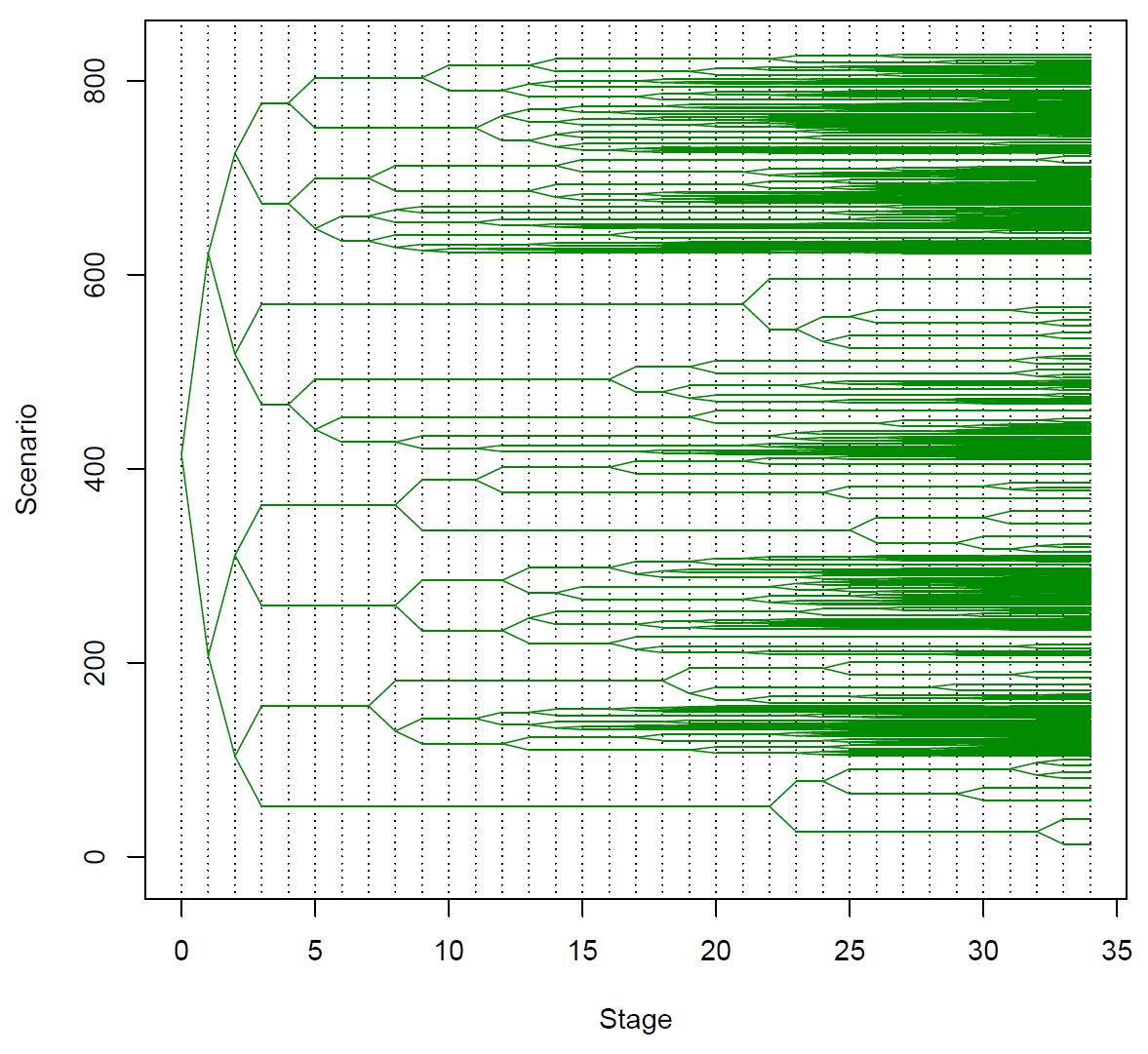 On November 30th 2020 took place the defense of the Ph.D. Thesis entittled " Multistage Scenario Trees Generation for Renewable Energy Systems Optimization", authored by Ms. Marlyn D. Cuadrado Guevara and advised by prof. F.-Javier Heredia. In this thesis a new methodology to generate and validate probability scenario trees for multistage stochastic programming problems arising in two different energy systems with renewables are proposed. The first problem corresponds to the optimal bid to electricity markets of a virtual power plant that consists on a wind-power plant plus a battery storage energy systems. The second one is the optimal operation of a distribution grid with some photovoltaic production.
Fri, 04/03/2020 - 11:42 — admin
| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2020 |
| Authors | Mattia Barbero; Cristina Corchero; Lluc Canals; Lucia Igualada; F.-Javier Heredia |
| Journal Title | Applied Energy |
| Volume | 264 |
| Journal Date | 04/2020 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| ISSN Number | 0306-2619/ |
| Key Words | Demand Aggregator; Regulatory framework; Ancillary Services; Demand Response; Tertiary building management; research; paper |
| Abstract | European Directives are incentivizing consumers to play an active role in the electricity system and to collaborate to maintain its stability, which has been historically provided by large generation power plants. However, it is not easy for the System Operator to handle the coexistence of consumers and generators in the same markets. Under these circumstances, a new actor allows small residential and commercial consumers to participate in flexibility markets: The Demand Aggregator. However, balancing markets opened to Demand Aggregators still present several barriers that do not allow their practical participation. This study analyzes barriers and enablers of four European electricity markets and proposes a new market framework that would enhance Demand Aggregators’ participation. To validate the proposed market and to understand the economic potentials of aggregated small tertiary buildings, a Demand Aggregator is simulated using real building’s consumption data. Results show that technical requirements to participate in balancing markets such as the minimum bid size, the symmetricity of the offer and the product resolution strongly affect incomes for Demand Aggregators. However, neither in the proposed market, the creation of a Demand Aggregator whose business model is focused on small tertiary buildings does not seem realistic due to low incomes in comparison to the fixed costs necessary to enable Demand Response, especially if only the air conditioning system is considered. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114707 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Wed, 07/11/2018 - 11:26 — admin
| Publication Type | Conference Paper |
| Year of Publication | 2018 |
| Authors | Cristina Corchero; Josep Homs-Moreno; F.-Javier Heredia; Lucia Igualada; Mikel de Prada |
| Conference Name | 23th International Symposium on Mathematical Programming |
| Conference Date | 01-06/07/2018 |
| Conference Location | Bordeaux |
| Type of Work | contributed presentation |
| Key Words | research; hybrid AC-DC; offshore wind power plant; local branching |
| Abstract | The current study analyses a hybrid o↵shore wind farm design in which individual wind turbine power converters are removed from wind turbines and are installed on intermediate o↵shore collector platforms. In this study a compact and small-sized mixedinteger linear optimisation model makes four decisions with the goal of minimising installation and operation costs: the location and the number of o↵shore platforms and power converters to be installed, the optimal wind farm cable layout and the cluster optimal operating frequency of each wind turbine. The solutions found either for small and large o↵shore wind farms improve notoriously real-world designs, reducing up to 8 percent installation and maintenance costs. On the optimization technical results, a variant of Local Branching has been developed, reducing in some cases more than half of computing time with respect to default Local Branching. The model developed serves as a mathematical tool to provide rigorous evidences of the suitability of the hybrid design versus traditional o↵shore wind farm designs. |
| URL | Click Here |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |
Tue, 05/15/2018 - 16:25 — admin
| Publication Type | Journal Article |
| Year of Publication | 2018 |
| Authors | F.-Javier Heredia; Marlyn D. Cuadrado; Cristina Corchero |
| Journal Title | Computers and Operations Research |
| Volume | 96 |
| Pages | 316-329 |
| Journal Date | 08/2018 |
| Publisher | Elsevier |
| ISSN Number | 0305-0548 |
| Key Words | research; Battery energy storage systems; Electricity markets; Ancillary services market; Wind power generation; Virtual power plants; Stochastic programming; paper |
| Abstract | The recent cost reduction and technological advances in medium- to large-scale battery energy storage systems (BESS) makes these devices a true alternative for wind producers operating in electricity markets. Associating a wind power farm with a BESS (the so-called virtual power plant (VPP)) provides utilities with a tool that converts uncertain wind power production into a dispatchable technology that can operate not only in spot and adjustment markets (day-ahead and intraday markets) but also in ancillary services markets that, up to now, were forbidden to non-dispatchable technologies. What is more, recent studies have shown capital cost investment in BESS can be recovered only by means of such a VPP participating in the ancillary services markets. We present in this study a multi-stage stochastic programming model to find the optimal operation of a VPP in the day-ahead, intraday and secondary reserve markets while taking into account uncertainty in wind power generation and clearing prices (day-ahead, secondary reserve, intraday markets and system imbalances). A case study with real data from the Iberian electricity market is presented. |
| URL | Click Here |
| DOI | 10.1016/j.cor.2018.03.004 |
| Preprint | http://hdl.handle.net/2117/118479 |
| Export | Tagged XML BibTex |

|

 On November 30th 2020 took place the defense of the Ph.D. Thesis entittled "Multistage Scenario Trees Generation for Renewable Energy Systems Optimization", authored by Ms. Marlyn D. Cuadrado Guevara and advised by prof. F.-Javier Heredia. In this thesis a new methodology to generate and validate probability scenario trees for multistage stochastic programming problems arising in two different energy systems with renewables are proposed. The first problem corresponds to the optimal bid to electricity markets of a virtual power plant that consists on a wind-power plant plus a battery storage energy systems. The second one is the optimal operation of a distribution grid with some photovoltaic production.
On November 30th 2020 took place the defense of the Ph.D. Thesis entittled "Multistage Scenario Trees Generation for Renewable Energy Systems Optimization", authored by Ms. Marlyn D. Cuadrado Guevara and advised by prof. F.-Javier Heredia. In this thesis a new methodology to generate and validate probability scenario trees for multistage stochastic programming problems arising in two different energy systems with renewables are proposed. The first problem corresponds to the optimal bid to electricity markets of a virtual power plant that consists on a wind-power plant plus a battery storage energy systems. The second one is the optimal operation of a distribution grid with some photovoltaic production.
 The work On optimal participation in the electricity markets of wind power plants with battery energy storage systems has been published in the journal Computers and Operations Research. We present in this study a multi-stage stochastic programming model to find the optimal operation of a VPP in the day-ahead, intraday and secondary reserve markets hile taking into account uncertainty in wind power generation and clearing prices (day-ahead, secondary reserve, intraday markets and system imbalances). A case study with real data from the Iberian electricity market is presented. Preprint available at http://hdl.handle.net/2117/118479
The work On optimal participation in the electricity markets of wind power plants with battery energy storage systems has been published in the journal Computers and Operations Research. We present in this study a multi-stage stochastic programming model to find the optimal operation of a VPP in the day-ahead, intraday and secondary reserve markets hile taking into account uncertainty in wind power generation and clearing prices (day-ahead, secondary reserve, intraday markets and system imbalances). A case study with real data from the Iberian electricity market is presented. Preprint available at http://hdl.handle.net/2117/118479
